-
[SWEA] 5644번 : 무선 충전 (JAVA)SWEA 2024. 5. 5. 22:09
https://swexpertacademy.com/main/code/problem/problemDetail.do?contestProbId=AWXRDL1aeugDFAUo
SW Expert Academy
SW 프로그래밍 역량 강화에 도움이 되는 다양한 학습 컨텐츠를 확인하세요!
swexpertacademy.com
겹치는걸 어떻게 처리하지...하다가 결국 풀이를 보기로 했다.
풀이를 보기 전 내 로직을 잠깐 보자면,
1. 우선 좌표를 이용해서 풀었는데, dx, dy 로 먼저 위치 이동 저장해두고
// 상 우 하 좌 1 2 3 4 static int dx[] = {0, -1, 0, 1, 0}; static int dy[] = {0, 0, 1, 0, -1};입력을 받는다.
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception, IOException { BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); StringTokenizer st; int T = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine()); for(int tc=1; tc<=T; tc++) { mp = new HashMap<>(); st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine()); M = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); // 총 이동 시간 A = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); // BC 의 개수 map = new int[11][11]; v = new int[11][11]; // 위치 : x, y st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine()); moveA = new int[M+1]; moveB = new int[M+1]; for(int i=1;i<=M;i++) { moveA[i] = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); } st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine()); for(int i=1;i<=M;i++) { moveB[i] = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); } // 충전 범위 : c // 성능 : p for(int i=0;i<A;i++) { st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine()); int x = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); int y = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); int c = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); int p = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); make(x, y, c, p, i+1); // map 에 충전 범위 표시 mp.put(i+1, p); // BC 마다 충전 양 저장 } for(int i=1;i<=10;i++) { for(int j=1;j<=10;j++){ System.out.print(map[i][j] + " "); } System.out.println(); } ans = solve(); System.out.println("#" + tc + " " + ans); } }moveA, moveB 에 이동 방향이 저장되어 있으니까 그걸 활용해서 매 초마다 이동 좌표를 저장 했다.
static int solve() { int sum=0; // A -> (0, 0) // B -> (9, 9) int ax=0, ay=0; int bx=9, by=9; for(int i=1;i<=M;i++) { // cal 함수 에서 return 한 걸 다 더해 주면 총 충전한 양 sum+=cal(ax, ay, bx, by); ax = ax + dx[moveA[i]]; ay = ay + dy[moveA[i]]; bx = bx + dx[moveB[i]]; by = by + dy[moveB[i]]; } return sum; }2. 이걸 가지고 매 초마다 충전한 A, B의 합을 구했는데, 처음 입력 받을 때 map 에 해당 BC 의 값과 충전 양을 저장해두어서
// 매 초 마다 충전한 A, B의 합 return static int cal(int ax, int ay, int bx, int by) { int total=0; // A 위치 값 : map[ax][ay] // B 위치 값 : map[bx][by] // 좌표에 따른 충전 양 // mp.get(map[ax][ay]); total += mp.get(map[ax][ay]) + mp.get(map[bx][by]); // 겹치는 것 중에서 충전 양이 더 큰 걸 선택 해야 하는데 // 겹치는 거 어떻게 처리 하지?...ㅠ return total; }그 key 의 value 값을 더해주었다. 근데 겹치는 거 처리를 못하겠다... ㅠㅠ
3. make 함수를 활용해서 map 에 BC 별로 저장해둔다.
static void make(int x, int y, int c, int p, int val) { map[x][y] = val; Queue<Node> q = new ArrayDeque<>(); q.add(new Node(x, y, 0, p)); v[x][y] = 1; while(!q.isEmpty()) { Node cur = q.poll(); int cc = cur.c; int cx = cur.x; int cy = cur.y; if(cc == c) { return; } for(int i=1;i<5;i++) { int nx = cx + dx[i]; int ny = cy + dy[i]; if(nx>=1 && nx<=10 && ny>=1 && ny<=10 && v[nx][ny]==0) { q.add(new Node(nx, ny, cc+1, p)); map[nx][ny]=val; v[nx][ny] = 1; } } } }근데 이미 방문한 곳은 이전걸로 저장되어있다...겹치는 거 처리가 문제...
cf. 이것도 있었는데, 쓰진 않았다.
static void print(int arr[][]) { for(int i=0;i<10;i++) { for(int j=0;j<10;j++) { System.out.print(arr[i][j] + " "); } System.out.println(); } } static int dis(int ax, int bx, int ay, int by) { return Math.abs(ax-bx) + Math.abs(ay-by); }내 전체코드는 이러했다...그러고 답을 봤지...
import java.io.*; import java.util.*; class Solution { static int M, A, ans=0; // 상 우 하 좌 1 2 3 4 static int dx[] = {0, -1, 0, 1, 0}; static int dy[] = {0, 0, 1, 0, -1}; static Map<Integer, Integer> mp; static int moveA[], moveB[], map[][], v[][]; public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception, IOException { BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); StringTokenizer st; int T = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine()); for(int tc=1; tc<=T; tc++) { mp = new HashMap<>(); st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine()); M = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); // 총 이동 시간 A = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); // BC 의 개수 map = new int[11][11]; v = new int[11][11]; // 위치 : x, y st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine()); moveA = new int[M+1]; moveB = new int[M+1]; for(int i=1;i<=M;i++) { moveA[i] = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); } st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine()); for(int i=1;i<=M;i++) { moveB[i] = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); } // 충전 범위 : c // 성능 : p for(int i=0;i<A;i++) { st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine()); int x = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); int y = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); int c = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); int p = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); make(x, y, c, p, i+1); // map 에 충전 범위 표시 mp.put(i+1, p); // BC 마다 충전 양 저장 } for(int i=1;i<=10;i++) { for(int j=1;j<=10;j++){ System.out.print(map[i][j] + " "); } System.out.println(); } ans = solve(); System.out.println("#" + tc + " " + ans); } } static int solve() { int sum=0; // A -> (0, 0) // B -> (9, 9) int ax=0, ay=0; int bx=9, by=9; for(int i=1;i<=M;i++) { // cal 함수 에서 return 한 걸 다 더해 주면 총 충전한 양 sum+=cal(ax, ay, bx, by); ax = ax + dx[moveA[i]]; ay = ay + dy[moveA[i]]; bx = bx + dx[moveB[i]]; by = by + dy[moveB[i]]; } return sum; } // 매 초 마다 충전한 A, B의 합 return static int cal(int ax, int ay, int bx, int by) { int total=0; // A 위치 값 : map[ax][ay] // B 위치 값 : map[bx][by] // 좌표에 따른 충전 양 // mp.get(map[ax][ay]); total += mp.get(map[ax][ay]) + mp.get(map[bx][by]); // 겹치는 것 중에서 충전 양이 더 큰 걸 선택 해야 하는데 // 겹치는 거 어떻게 처리 하지?...ㅠ return total; } static void make(int x, int y, int c, int p, int val) { map[x][y] = val; Queue<Node> q = new ArrayDeque<>(); q.add(new Node(x, y, 0, p)); v[x][y] = 1; while(!q.isEmpty()) { Node cur = q.poll(); int cc = cur.c; int cx = cur.x; int cy = cur.y; if(cc == c) { return; } for(int i=1;i<5;i++) { int nx = cx + dx[i]; int ny = cy + dy[i]; if(nx>=1 && nx<=10 && ny>=1 && ny<=10 && v[nx][ny]==0) { q.add(new Node(nx, ny, cc+1, p)); map[nx][ny]=val; v[nx][ny] = 1; } } } } static void print(int arr[][]) { for(int i=0;i<10;i++) { for(int j=0;j<10;j++) { System.out.print(arr[i][j] + " "); } System.out.println(); } } static int dis(int ax, int bx, int ay, int by) { return Math.abs(ax-bx) + Math.abs(ay-by); } } class Node{ int x; int y; int c; int p; Node(int x, int y, int c, int p){ this.x = x; this.y = y; this.c = c; this.p = p; } }https://diane21.tistory.com/35
[SWEA-5644] 무선 충전
https://swexpertacademy.com/main/code/problem/problemDetail.do?contestProbId=AWXRDL1aeugDFAUo SW Expert Academy SW 프로그래밍 역량 강화에 도움이 되는 다양한 학습 컨텐츠를 확인하세요! swexpertacademy.com 이 문제는 SWEA에
diane21.tistory.com
나랑 가장 비슷한 풀이로...
1. solve 함수 변경
원래 map 을 활용하려고 했을 때는 index 0 부터 시작했지만, 받아오는 값이 달라져서 (1,1), (10, 10) 에서 시작하는걸로 변경했다.
static int solve() { int sum=0; // A -> (1, 1) // B -> (10, 10) // 처음 위치에 대한 경우 (0초) int ax=1, ay=1; int bx=10, by=10; sum+=cal(ax, ay, bx, by); // 1초 부터 cal for(int i=1;i<=M;i++) { ax = ax + dx[moveA[i]]; // A의 x 좌표 ay = ay + dy[moveA[i]]; // A의 y 좌표 bx = bx + dx[moveB[i]]; // B의 x 좌표 by = by + dy[moveB[i]]; // B의 y 좌표 // cal 함수 에서 return 한 걸 다 더해 주면 총 충전한 양 sum+=cal(ax, ay, bx, by); } return sum; }2. 거리 함수 활용
괜히 거리구하는걸 준게 아니다. 넘겨준 BC 에 해당하는 위치부터, A, B 간의 거리를 구한다.
static int disCheck(int idx, int x, int y) { // 충전기 에서 (x, y) 까지 거리가 충전 할 수 있는 거리 라면 // 충전 량을 보내 주고, // 충전을 못 한다면 0 return return Math.abs(listBC.get(idx).x-x) + Math.abs(listBC.get(idx).y-y) <= listBC.get(idx).c ? listBC.get(idx).p : 0; }3. 계산하는 방식 변경
거리함수에서 보면 어짜피 충전 못하면 0을 리턴해버린다. 그래서 두 충전소가 다르다면 그냥 더해주면 되고, 이런식으로 순열/조합을 사용하면 편하다는걸...풀이 보고 알았다..!
그리고 충전소가 같다면 어짜피 절반으로 나누니까, 그냥 큰 값을 저장해버리면 된다.

C1 이 100 이고 C3 가 70 일때,
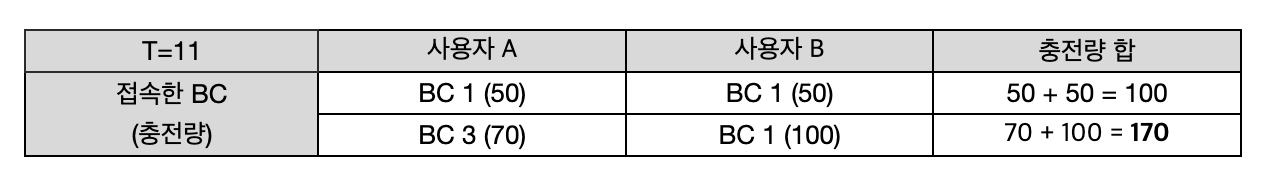
A, B 합을 보면 100이다. 즉, C1의 원래 충전량인거다. 그래서 그냥 그 값을 sum 으로 두면 된다. (절반 나눈 효과)
// 매 초 마다 충전한 A, B의 합 return static int cal(int ax, int ay, int bx, int by) { int total=0; for(int a=0;a<listBC.size();a++) { for(int b=0;b<listBC.size();b++) { int sum=0; int aSum = disCheck(a, ax, ay); int bSum = disCheck(b, bx, by); // 두 충전소 다르면 충전량 나누지 X if(a != b) { // disCheck 함수 에서 충전 불가능 하면 0 을 return 하므로 sum += aSum + bSum; }else { // 충전소 같으면 둘 중 큰 값 sum = Math.max(aSum, bSum); } // sum 이 가장 큰 값 찾기 total = Math.max(total, sum); } } return total; }그렇게까지 하면 최종코드는 아래와 같다.
[최종 코드]
import java.io.*; import java.util.*; class Solution { static int M, A, ans=0; // 상 우 하 좌 1 2 3 4 static int dy[] = {0, -1, 0, 1, 0}; static int dx[] = {0, 0, 1, 0, -1}; static int moveA[], moveB[]; static List<Node> listBC; public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception, IOException { BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in)); StringTokenizer st; int T = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine()); for(int tc=1; tc<=T; tc++) { listBC = new ArrayList<>(); st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine()); M = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); // 총 이동 시간 A = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); // BC 의 개수 // 위치 : x, y st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine()); moveA = new int[M+1]; moveB = new int[M+1]; for(int i=1;i<=M;i++) { moveA[i] = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); } st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine()); for(int i=1;i<=M;i++) { moveB[i] = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); } // 충전 범위 : c // 성능 : p for(int i=0;i<A;i++) { st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine()); int x = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); int y = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); int c = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); // 거리 int p = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()); // 충전량 listBC.add(new Node(x, y, c, p)); // BC 정보 저장 list } ans = solve(); System.out.println("#" + tc + " " + ans); } } static int solve() { int sum=0; // A -> (0, 0) // B -> (9, 9) // 처음 위치에 대한 경우 (0초) int ax=1, ay=1; int bx=10, by=10; sum+=cal(ax, ay, bx, by); // 1초 부터 cal for(int i=1;i<=M;i++) { ax = ax + dx[moveA[i]]; // A의 x 좌표 ay = ay + dy[moveA[i]]; // A의 y 좌표 bx = bx + dx[moveB[i]]; // B의 x 좌표 by = by + dy[moveB[i]]; // B의 y 좌표 // cal 함수 에서 return 한 걸 다 더해 주면 총 충전한 양 sum+=cal(ax, ay, bx, by); } return sum; } // 매 초 마다 충전한 A, B의 합 return static int cal(int ax, int ay, int bx, int by) { int total=0; for(int a=0;a<listBC.size();a++) { for(int b=0;b<listBC.size();b++) { int sum=0; int aSum = disCheck(a, ax, ay); int bSum = disCheck(b, bx, by); // 두 충전소 다르면 충전량 나누지 X if(a != b) { // disCheck 함수 에서 충전 불가능 하면 0 을 return 하므로 sum += aSum + bSum; }else { // 충전소 같으면 둘 중 큰 값 sum = Math.max(aSum, bSum); } // sum 이 가장 큰 값 찾기 total = Math.max(total, sum); } } return total; } static int disCheck(int idx, int x, int y) { // 충전기 에서 (x, y) 까지 거리가 충전 할 수 있는 거리 라면 // 충전 량을 보내 주고, // 충전을 못 한다면 0 return return Math.abs(listBC.get(idx).x-x) + Math.abs(listBC.get(idx).y-y) <= listBC.get(idx).c ? listBC.get(idx).p : 0; } } class Node{ int x; int y; int c; // 거리 int p; // 충전량 Node(int x, int y, int c, int p){ this.x = x; this.y = y; this.c = c; this.p = p; } }'SWEA' 카테고리의 다른 글
[SWEA] 2105번 : 디저트 카페 (0) 2024.05.18 [SWEA] 4012번 : 요리사 (0) 2024.05.16 [SWEA] 5656번 : 벽돌 깨기 (JAVA) (0) 2024.05.03 [SWEA] 2115번 : 벌꿀 채취 (JAVA) (0) 2024.05.02 [SWEA] 논리와증명 / 수와 표현 (문제풀이) (2) 2024.01.14